Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health. With diabetes and insulin resistance affecting millions of Americans and approximately 537 million adults worldwide, according to the International Diabetes Federation effective blood glucose management is essential.
While medications remain a necessity for many, natural approaches offer valuable support for healthy glucose metabolism. Whether you have diabetes, prediabetes, or simply want to optimize metabolic health, incorporating dietary aids and lifestyle modifications can make a significant difference.
Let us explore evidence-based natural ingredients, dietary strategies, and monitoring techniques to help you manage blood sugar naturally:
Understanding Blood Sugar Fundamentals
Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. By recognizing how your diet, stress levels, sleep quality, physical activity, and medications influence glucose regulation, you can make more informed choices to support your overall health. In some cases, blood sugar supplements can provide additional support in maintaining healthy glucose levels. Next, let’s explore practical strategies for managing blood sugar effectively.
The Science Behind Glucose Regulation
Your body maintains blood glucose levels within a specific range typically 70-100 mg/dL when fasting. This balance involves hormones like insulin and glucagon. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose for energy, while glucagon signals the liver to release stored glucose when levels drop.
When insulin resistance or reduced insulin production occurs, blood sugar levels can remain elevated, posing risks to blood vessels and nerves.
Common Causes of Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Factors that impact blood sugar include:
- Dietary Choices: Refined carbohydrates and sugary foods cause spikes, while proteins, fats, and fiber slow absorption.
- Stress: Cortisol release increases blood sugar. Studies indicate that 47% of adults report stress-related blood sugar changes.
- Sleep Quality: Poor sleep can reduce insulin sensitivity by up to 25%.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, while inactivity worsens it.
- Medications: Certain steroids and antipsychotics may raise blood sugar.

Dietary Strategies for Balanced Glucose Levels
The overall health benefits of controlled glucose levels can be supported by learning about the glycemic index as a method to guide your food choices. Expert studies show that foods with GI levels below 55 produce gradual blood sugar peaks in human bodies. Non-starchy vegetables and berries along with whole grains make up examples of low GI foods. Various foods with a medium GI of 56 to 69 include brown rice and whole wheat bread and sweet potatoes thus leading to moderate blood sugar changes. The blood sugar patterns of high GI foods featuring ratings above 70 points trigger swift spikes in sugar levels in the bloodstream.
Fiber stands as a vital substance that controls blood sugar levels. The presence of fiber controls the rate of glucose absorption while making insulin more effective to reach constant blood sugar regulation. Medical authorities state that people should get their daily fiber intake from 25 to 30 grams by eating foods such as vegetables (broccoli, leafy greens), berries, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Some superfoods provide additional benefits for glucose management. A daily intake of 1-2 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar prior to meals demonstrates its ability to enhance insulin functions while controlling blood sugar irregularities. The compounds found in bitter melon duplicate the effects of insulin which makes it an advantageous substance for managing blood sugar levels. The consumption of fenugreek seeds in any form including soaked and ground forms helps decrease glucose spikes while sustaining metabolic well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications for Blood Sugar Management
Making lifestyle adjustments can significantly enhance blood sugar management. From meal timing to physical activity and stress management, adopting these habits can support better glucose control and overall well-being. Here’s how you can incorporate these strategies into your daily routine.
Strategic Meal Timing and Portion Control
- Maintain a consistent meal schedule
- Practice portion control and mindful eating
- Consume higher-calorie meals earlier in the day for better glucose response
Exercise for Optimal Blood Sugar
The CDC recommends 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly to reduce type 2 diabetes risk. Post-meal walks can lower glucose spikes by 30-45%.
- Combine cardio and strength training
- Time workouts within 30-60 minutes after meals for maximum impact
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress increases cortisol, raising blood sugar. Effective techniques include:
- Meditation and deep breathing
- Physical activity
- Adequate sleep (7-9 hours)
- Social connections

Monitoring Progress: Tools and Techniques
Monitoring blood sugar levels at home is a crucial part of managing glucose effectively. Various devices and tracking methods provide valuable insights into how your body responds to food, activity, and other lifestyle factors. By consistently using these tools, you can make informed decisions to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Home Monitoring Devices
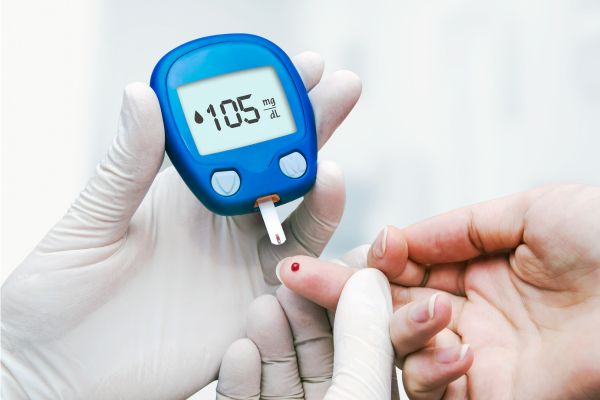
- Glucose Meters: These handheld devices offer point-in-time blood sugar readings using a small drop of blood from a finger prick. They are reliable for routine monitoring, especially before and after meals or during times when blood sugar fluctuations are expected.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs provide real-time data on glucose levels through a small sensor placed under the skin. They track glucose levels continuously, offering detailed insights into patterns and trends throughout the day and night. Many CGMs send alerts for sudden spikes or drops, making them particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
- Apps and Wearables: Some advanced wearable devices and smartphone apps estimate glucose trends using data from fitness trackers, diet logs, and activity levels. While they don’t replace direct glucose measurements, they can offer a broader view of how lifestyle factors affect blood sugar.
Tracking Methods
- Food and Symptom Journal: A written or digital Food and Symptom Journal enables users to track their meals as well as physical activity along with stress levels and symptoms they observe. People can recognize blood sugar-level influencing patterns and triggers through this monitoring method.
- Digital Tracking Tools: Digital tracking tools enable mobile apps which automatically synchronize glucose meter and CGM readings through integrative tracking platforms. The tools produce visual representations of glucose patterns through reporting systems that facilitate better understanding of improvement areas.
- Systematic Food Response Testing: Getting blood sugar measurements before eating certain foods and at the time directly after consumption will show you the impact different foods have on your glucose levels. Comparison between blood sugar readings will help you create a diet plan that incorporates foods which maintain better blood sugar control.
The ability to manage your glucose levels actively occurs through reliable blood glucose tracking using established methods. Healthier choices can be made based on your data insights which enables you to receive custom adjustments in your nutrition plan and activity regimen and life approach.
Conclusion
Natural blood sugar monitoring depends on dietary aids which are combined with lifestyle modifications while monitoring value changes regularly. The combination of cinnamon and berberine treatment along with individualized diet choices and exercise protocols allows people to achieve better metabolic health control.
Work with a healthcare provider before making major alterations particularly when you need medication. The described steps can help you determine the most effective measures for maintaining stable blood sugar while promoting lasting health benefits.
FAQs
What are the best foods to eat for balanced blood sugar levels?
Low GI foods like non-starchy vegetables, berries, whole grains, and fiber-rich options help stabilize blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar at home?
Frequency varies based on your health condition. For diabetes management, checking before and after meals or using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is recommended.
Can stress and poor sleep affect blood sugar levels?
Yes, chronic stress increases cortisol, which raises blood sugar. Poor sleep also reduces insulin sensitivity, making stress management and quality sleep essential for glucose control.




