

How to Create an Amortization Schedule?
As the fintech industry expands to become ever larger and more complex, the financial industry as a whole has shifted– both for business and individuals– to one where the borrower is in control.
For this reason, it’s as important as ever to be able to understand what you’re getting yourself into when you finance anything– whether that’s a mortgage on a house, credit card, or business loan.
Interest, in particular, is critical to understand. Even a 1% difference in interest can mean thousands of dollars. And, often, the details of those terms can cost you much more.
That’s why knowing how to create an amortization schedule is crucial if you hope to accurately estimate how much you’ll pay in interest over time and whether a particular form of credit or financing is worth it.
What is an amortization schedule & why is knowing how to create one important?
 What is an amortization schedule and what does it have to do with understanding interest rates?
What is an amortization schedule and what does it have to do with understanding interest rates?
An amortization schedule is a schedule of payments which shows the breakdown between principal and interest. In other words, with an amortization schedule, you know exactly how much of a given payment is going towards interest and how much is going towards your principal.
Understanding how an amortization schedule works and knowing how to create one for reference is useful for several reasons. One common use is to calculate when would be best to refinance a property, whether business or personal residence.
In addition to this, an amortization schedule can help you figure out how long you’ll be upside down on a vehicle loan. That’s because while all payments for most types of financing are the same, the percentage that goes into interest is usually higher at the beginning of a loan while more of each payment goes into principal as the loan ages.
And it can also help you determine if a business loan or credit card has favorable terms before making a costly financial misstep.
How to create an amortization schedule
Amortization is calculated slightly different depending on the industry and type of financing, but the general equation is always the same.
The most effective route is to obtain the amortization schedule of the type of financing in question. However, if that isn’t available, you can make your own using your payment schedule and interest rate in a program such as Microsoft Excel.
For example, let’s look at a $100,000.00 loan with:
Interest rate ÷ Interest method
Interest method is likely annual, however, monthly is also a common method. If the interest method is annual, the calculation is:
4% ÷ 12 = .00333 (or .33%, a third of one percent)
With that information, you’re able to take the $100,000.00 loan balance and divide it by .00333 to get the percentage of your regular loan payment that equals interest. In this case, about $333 of your regular payment goes towards interest:
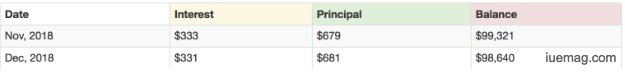
With your interest calculation, you’re able to then subtract that $333 from your $1,012.00 payment to get the amount which goes toward principal: roughly $679.00.
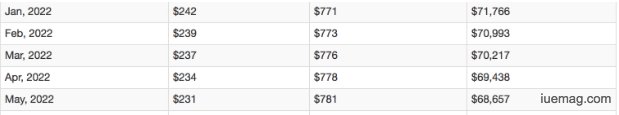
By applying that interest percentage to the new reduced loan balance after each proceeding payment, as the balance lowers the amount you pay in interest lowers. For example, 3 years later after 38 payments, the amount that goes toward interest each month is just $242, a whole $91 less than when you first started making payments:
By understanding the effects of long-term interest, you’ll be able to more properly forecast your long-term investment and whether you’re getting a deal that makes sense.
For this reason, it’s as important as ever to be able to understand what you’re getting yourself into when you finance anything– whether that’s a mortgage on a house, credit card, or business loan.
Interest, in particular, is critical to understand. Even a 1% difference in interest can mean thousands of dollars. And, often, the details of those terms can cost you much more.
That’s why knowing how to create an amortization schedule is crucial if you hope to accurately estimate how much you’ll pay in interest over time and whether a particular form of credit or financing is worth it.
What is an amortization schedule & why is knowing how to create one important?
 What is an amortization schedule and what does it have to do with understanding interest rates?
What is an amortization schedule and what does it have to do with understanding interest rates?An amortization schedule is a schedule of payments which shows the breakdown between principal and interest. In other words, with an amortization schedule, you know exactly how much of a given payment is going towards interest and how much is going towards your principal.
Understanding how an amortization schedule works and knowing how to create one for reference is useful for several reasons. One common use is to calculate when would be best to refinance a property, whether business or personal residence.
In addition to this, an amortization schedule can help you figure out how long you’ll be upside down on a vehicle loan. That’s because while all payments for most types of financing are the same, the percentage that goes into interest is usually higher at the beginning of a loan while more of each payment goes into principal as the loan ages.
And it can also help you determine if a business loan or credit card has favorable terms before making a costly financial misstep.
How to create an amortization schedule
Amortization is calculated slightly different depending on the industry and type of financing, but the general equation is always the same.The most effective route is to obtain the amortization schedule of the type of financing in question. However, if that isn’t available, you can make your own using your payment schedule and interest rate in a program such as Microsoft Excel.
For example, let’s look at a $100,000.00 loan with:
- 10-year term
- 4% interest rate
- And $1,012.00 monthly payment.
Interest rate ÷ Interest method
Interest method is likely annual, however, monthly is also a common method. If the interest method is annual, the calculation is:
4% ÷ 12 = .00333 (or .33%, a third of one percent)
With that information, you’re able to take the $100,000.00 loan balance and divide it by .00333 to get the percentage of your regular loan payment that equals interest. In this case, about $333 of your regular payment goes towards interest:

With your interest calculation, you’re able to then subtract that $333 from your $1,012.00 payment to get the amount which goes toward principal: roughly $679.00.
By applying that interest percentage to the new reduced loan balance after each proceeding payment, as the balance lowers the amount you pay in interest lowers. For example, 3 years later after 38 payments, the amount that goes toward interest each month is just $242, a whole $91 less than when you first started making payments:

By understanding the effects of long-term interest, you’ll be able to more properly forecast your long-term investment and whether you’re getting a deal that makes sense.
Copyrights © 2025 Inspiration Unlimited - iU - Online Global Positivity Media
Any facts, figures or references stated here are made by the author & don't reflect the endorsement of iU at all times unless otherwise drafted by official staff at iU. A part [small/large] could be AI generated content at times and it's inevitable today. If you have a feedback particularly with regards to that, feel free to let us know. This article was first published here on 29th November 2018.
Overthinking? Uninspired? Brain Fogged?
Let's Reset That! Try iU's Positivity Chat NOW!

All chats are end-to-end encrypted by WhatsApp and won't be shared anywhere [won't be stored either].


